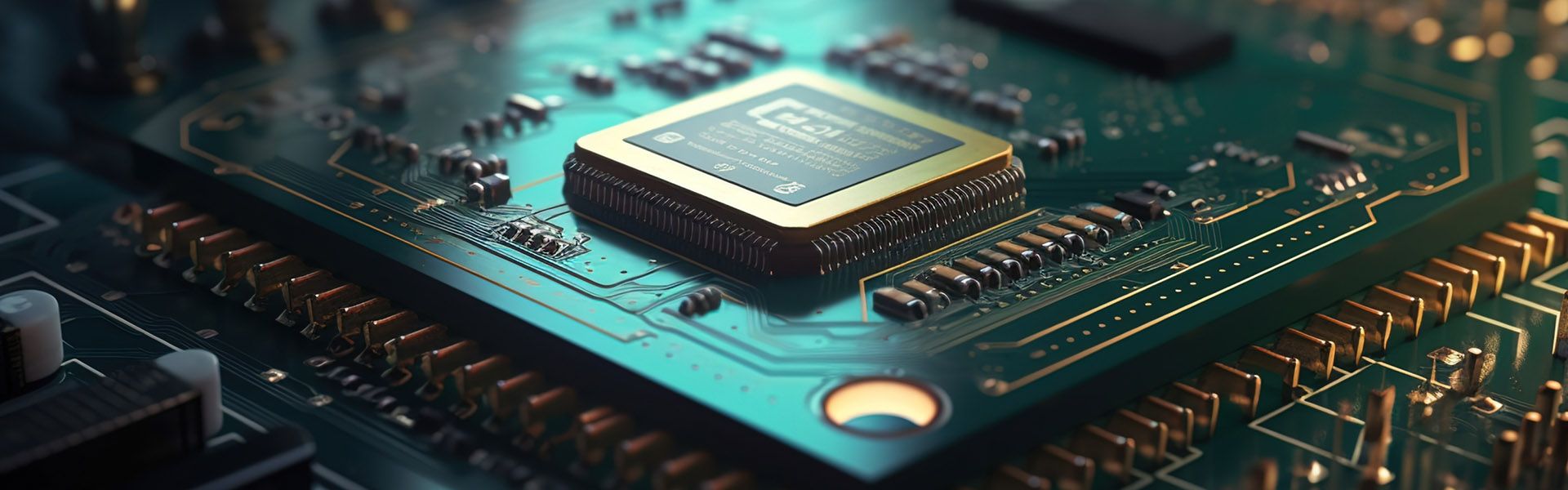
What is the role of SMT Lab?
In the world of electronics manufacturing, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) plays a crucial role in the production of modern electronic devices. At the heart of this process is the SMT Laboratory, an essential facility within a factory that ensures the precision, quality, and efficiency of electronic assembly.
What Is SMT?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to the method of mounting and soldering electronic components directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). This process is widely used in the production of LED drivers, power supplies, and various consumer electronics due to its ability to produce highly reliable, compact, and cost-effective electronic assemblies.
The Role of the SMT Lab
An SMT lab is where the SMT process is tested, fine-tuned, and optimized before mass production begins. This laboratory environment is equipped with advanced machines and testing equipment to simulate the entire SMT production process under controlled conditions. Here are the main functions of an SMT lab:
Prototype Development:
Before large-scale production begins, prototypes of PCBs or electronic components are assembled in the SMT lab. This allows the factory to evaluate the design, identify any potential issues, and make necessary adjustments before committing to mass production. It’s a crucial step in ensuring that the product design is not only functional but also optimized for large-scale assembly.
Process Testing and Validation:
The SMT lab is responsible for testing and validating the manufacturing process itself. Engineers can test various configurations, solder paste applications, component placement strategies, and reflow oven profiles to ensure the production line is running at peak efficiency. This helps prevent costly errors that could occur during mass production, such as improper component alignment or poor solder joints.
Quality Control:
Quality control is one of the most important tasks in the SMT lab. Using advanced inspection tools such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray testing, engineers can detect defects like misaligned components, soldering issues, or other production inconsistencies. By catching these issues early in the lab, the factory ensures that only high-quality, defect-free products reach the customer.
Performance Testing:
After the PCB assembly is complete, the SMT lab conducts various performance tests to ensure that the final product meets all necessary standards and specifications. These tests include electrical performance checks, thermal cycling, and stress testing, which are vital for ensuring long-term reliability and durability of the product in the field.
Continuous Improvement:
The SMT lab also plays a critical role in continuously improving the manufacturing process. By analyzing data from each production run and identifying areas for optimization, the lab can make adjustments to increase yield rates, reduce waste, and improve overall product quality. This proactive approach to problem-solving helps the factory stay competitive and meet the ever-evolving demands of the electronics industry.
Conclusion
An SMT lab is far more than just a testing environment—it is an essential part of the overall production workflow. Its purpose is to guarantee that products are not only fully functional but also built with durability and precision, meeting the stringent requirements of the modern electronics industry. At our factory, the SMT lab plays a pivotal role in ensuring every product we manufacture embodies quality, innovation, and consistency. By thoroughly examining and refining each step of the assembly process, we are able to deliver solutions that meet our customers' exacting standards and provide reliable performance.
Let’s have a look the video of our SMT Lab:https://www.youtube.com/shorts/-Pjd69KBjOo
 EN
EN AR
AR NL
NL FR
FR DE
DE EL
EL HI
HI IT
IT KO
KO PL
PL PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES TL
TL IW
IW ID
ID UK
UK VI
VI HU
HU TH
TH TR
TR FA
FA MS
MS SW
SW AZ
AZ UR
UR BN
BN KK
KK